Image name: Sanity and Her Son Among the Credulous
Source: naked capitalism
As US Prepares to Ban Ivermectin for Covid-19, More Countries in Asia Begin Using It
The information war takes a dark turn as the corporate media transitions from misinformation and obfuscation to outright lies and fabrication.
The campaign against ivermectin is intensifying in the US. Until recently the health authorities appeared to be quite content merely to ridicule those who take or prescribe the drug in order to treat or prevent Covid-19. A couple of weeks ago, the FDA released a now-infamous advertorial on twitter with the heading “You are not a horse. You are not a cow. Seriously, y’all. Stop it.” The subheading: “Using the drug Ivermectin to treat Covid-19 can be dangerous and even lethal. The FDA has not approved the drug for that purpose.”
It’s a subtle message that has been faithfully echoed by the corporate media: ivermectin, a tried-and-tested drug that has won its discoverers a Nobel Prize for the impact it has had on human health over the last 35 years, should only be given to animals. But now the information war is taking a darker turn, as the media transitions from misinformation and obfuscation to outright lies and fabrication.
At the end of last week, a string of American and British outlets, including The Daily Mail, Rolling Stone, Huffington Post, The Independent, Newsweek, The Guardian, and Yahoo News, ran a story about how people who had “overdosed” on the “horse dewormer” were clogging up so many beds in a hospital in Sequoyah, rural Oklahoma, that doctors were having to turn away gunshot victims. The story, sourced to local Oklahoma outlet KFOR, turned out to be completely false. On Sunday, the hospital in question released a statement that the doctor behind the allegations had not worked in its ER for two months. More to the point, the hospital “had not treated any patients due to complications relating to taking ivermectin.” There were no overdoses. And it had turned no patients away.
In other words, everything about the story was false. A total fabrication. Yet many of the mainstream outlets that covered the story did not retract their article. Rolling Stone simply “updated” its piece with the new information. The Guardian inserted a note at the bottom of its article informing readers that Sequoyah NHS had released a statement asserting that the doctor behind the allegations that formed the entire basis of the story had not worked in its ER for two months. In other words, you have to read all the way to the end of the article to find out that its entire content is total bullshit. To make matters worse, The Guardian did not even mention the hospital’s categorical denials that it had treated patients for IVM overdose or that it had turned ER patients away.
The Coming Crack Down
If the goal of all this disinformation is to put people off wanting to get hold of ivermectin, it doesn’t seem to be working, which is hardly surprising given the already desperately low levels of public trust in both US health authorities and corporate media.
There are certain parallels with the furore whipped up over hydroxychloroquine last year. But the case is weaker this time, primarily because IVM is one of the safest medicines on the planet and was widely recognised as such until this pandemic.
One thing that is abundantly clear is that mocking people’s intelligence and comparing them to horses or dogs for wanting to take a certain medicine isn’t a terribly effective way of getting them to change their behaviour. All they appear to have achieved is to invoke the “Streisand effect.” More people are buying ivermectin (for human use) than ever before. In the US as a whole, prescriptions for the medicine have surged 24-fold since the pandemic began, from 3,600 a week to almost 90,000. Between mid-July and mid-August alone, they rose 400%.
In response, authorities are escalating their crack down. On September 1, the American Medical Association (AMA), American Pharmacists Association (APhA), and American Society of Health-System Pharmacists (ASHP) jointly called for an outright ban on the dispensing of ivermectin to prevent or treat COVID-19 outside of a clinical trial.
We are alarmed by reports that outpatient prescribing for and dispensing of ivermectin have increased 24-fold since before the pandemic and increased exponentially over the past few months. As such, we are calling for an immediate end to the prescribing, dispensing, and use of ivermectin for the prevention and treatment of COVID-19 outside of a clinical trial. In addition, we are urging physicians, pharmacists, and other prescribers—trusted health care professionals in their communities—to warn patients against the use of ivermectin outside of FDA-approved indications and guidance, whether intended for use in humans or animals, as well as purchasing ivermectin from online stores. Veterinary forms of this medication are highly concentrated for large animals and pose a significant toxicity risk for humans.
Demonising a “Wonder Drug” (Not My Words)
While it is true that ivermectin was first commercialised as a product for animal health in 1981, fast becoming one of the world’s biggest selling veterinary drugs, it has been used to treat humans since 1987. But most of those humans were in poor countries. As a 2017 article in Nature noted, ivermectin, perhaps more than any other drug, “is a drug for the world’s poor. For most of this century, some 250 million people have been taking it annually to combat two of the world’s most devastating, disfiguring, debilitating and stigma-inducing diseases, Onchocerciasis and Lymphatic filariasis”
“Ivermectin was a revelation. It had a broad spectrum of activity, was highly efficacious, acting robustly at low doses against a wide variety of nematode, insect and acarine parasites. It proved to be extremely effective against most common intestinal worms (except tapeworms), could be administered orally, topically or parentally and showed no signs of cross-resistance with other commonly used anti-parasitic compounds.”
Since the late ´80s more than 3.7 billion doses have been distributed globally in mass drug administration campaigns. All 3.7 billion of those doses were provided free of charge by the medicine’s developer, Merck. The company knew it would not be able to generate profits or even cover costs by selling the drug in the poverty-stricken communities afflicted by the two parasites, so it gave it away. “As much as needed for as long as needed” was the motto. It was a remarkable — and exceptionally rare — gift of generosity from a major pharmaceutical company.
Later on, it was discovered that ivermectin had many other properties. Using the drug as a long-term preventive against onchocerciasis had reduced the prevalence of other parasitic worms known as soil-transmitted helminths, which infect up to 20% of the world’s population and are a common cause of malnutrition and growth impairment in children. It was also discovered to have potent anti-viral effects.
After being used billions of times, this (in the words of Nature magazine) “enigmatic, multifaceted wonder drug” has been shown to have “an extremely good safety profile” — again Nature‘s words — as well as potential applications against a broad spectrum of diseases, from African trypanosomiasis (sleeping sickness) to schistosomiasis, one of the world’s most neglected tropical diseases that afflicts more than 200 million people worldwide; to asthma and epilepsy; to a host of RNA viruses including Zika, dengue, yellow fever, West Nile, chikungunya and HIV. It also appears to have potent anti-cancer properties.
Today, the FDA, with a little help from the media, is doing everything it can to destroy ivermectin’s reputation. At the same time, authorities appear to be clamping down on the importation, distribution and sales of the medicine. They are also beginning to crack down on doctors who have been prescribing the drug, regardless of how much success they’ve had with it.
A Whole Different Story Half a World Away
In Asia, the situation could not be more different. In India the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) — the most important biomedical research body in India and one of the oldest and largest medical research institutes in the world — has added ivermectin in its indication for Covid-19 to its list of essential medicines.
In June, one of three national health regulator in India, the Directorate General of Health Services, (DGHS) overhauled its COVID-19 treatment guidelines and removed almost all of the repurposed medicines it had previously recommended for treating asymptomatic and mild cases, including ivermectin. This sparked concerns that India was about to reverse its approval of ivermectin as a covid treatment. But to their credit, India’s two most important national health regulators — the All India Institute of Medical Science (AIIMS) and the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) — maintained their authorisation of ivermectin.
It’s hard to keep track of just how many states in India continue to use ivermectin as a treatment or prophylaxis against covid-19. Three states that are definitely using it are Uttar Pradesh (population: 230 million), Goa and Bihar (population: 100 million), a copy of whose home quarantine treatment program can be seen here. So, too, is New Delhi.
Though the usual caveats apply about numbers being under-reported due to inadequate testing, it’s clear that things have improved across India. Since the country began its last wave of infections, in March, no state has contained the virus as effectively as Uttar Pradesh, India’s most populous region with 230 million inhabitants. If it were a country, UP would be the world’s sixth most populous, sandwiched between Pakistan (5th) and Nigeria (7th). UP has been using IVM longer than any other Indian state, including as a prophylaxis for people who come in contact with the disease. The numbers (both in terms of cases and deaths) speak for themselves. The average number of cases per day over the last seven days was just 28 — in a region with a population larger than Brazil’s! Brazil’s daily average is more than 21,000 cases.
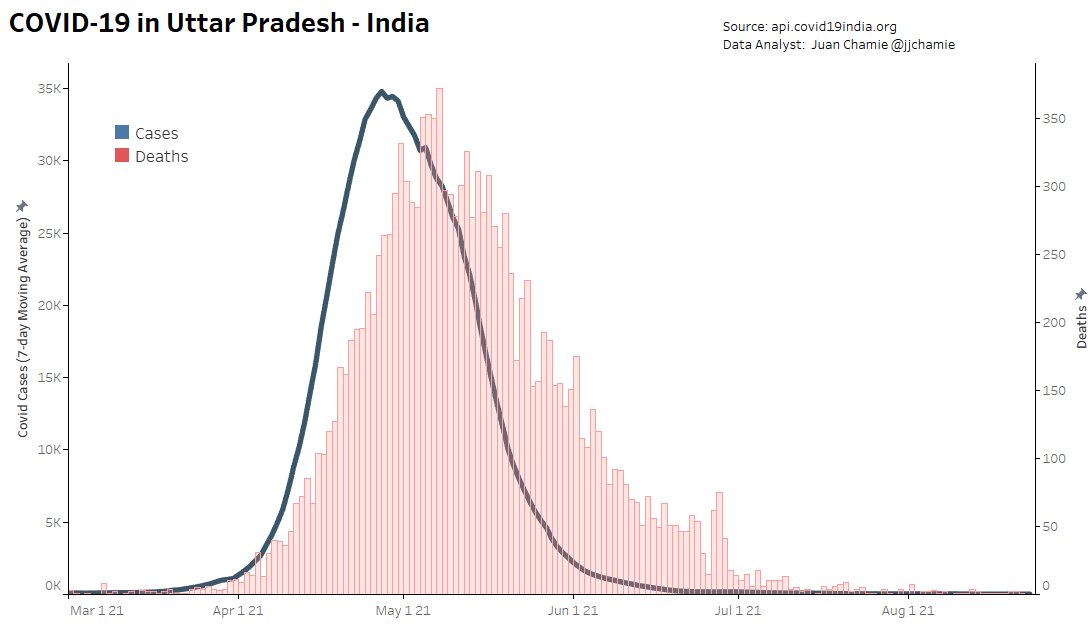
It’s a similar story in New Delhi, where the number of new cases is also close to zero.
Compare that to the state of Kerala, which has stopped prescribing ivermectin and other proven therapeutics and is making exhaustive use of Gilead’s largely ineffective (yet excruciatingly expensive) antiviral, remdesivir. Not only have case numbers barely declined from their mid-May peak but they are rising faster than in any other region. Despite boasting just 3% of India’s population, having one of the most advanced health systems in the country and one of the highest vaccination rates (over 50% of the population has received at least one dose), Kerala accounted for 62% of all of India’s Covid-19 cases in early August. The BBC described the region’s stubbornly high numbers as a “mystery”.
In India, nothing is quite as simple as it might seem, says Jerri-Lynn, who knows a thing or two about the subcontinent, having visited there for long periods:
UP is a large, rural state, with a still largely agrarian economy. It’s part of the northern Indian ‘cow belt’, with low literacy rates, and a distorted sex ratio. It’s the second poorest state in India in terms of per capita income. Kerala is much richer, and has more of a service-based economy; lots of Keralites work in the Gulf states and many send remittances back home. The state has been governed by successive left-wing governments for decades, has high literacy rates, the top female sex ratio in India, and some of its best medical care, particularly on the public health side.
As I mentioned to you before, I believe Kerala recorded the first covid case in India, in a female medical student returning from China — perhaps Wuhan in Jan 2020. The state initially did a good job managing covid and was held up as an exemplar; their contact tracing system was widely praised.
The UP government is notorious for its corruption. Many would take any official UP state figures with large fistfuls of salt. This is not the case for Kerala.
Kerala has by far the highest number of cases in the country while UP has the lowest, but is that because it is testing more and being more honest about the numbers? According to many mainstream reports (including Times of India and India Today), UP is doing more testing than any other state. Can that be true or is UP’s regional government doctoring the numbers? Or is it simply doing a very good job at keeping the virus contained, just like Mexico’s poorest region, Chiapas?
In India’s last brutal wave the turnaround in Uttar Pradesh was so dramatic that even the World Health Organization (WHO) showcased its achievements. In a May 7 article titled “Going the Last Mile to Stop Covid-19” the WHO noted that aggressive population-wide health schemes, including home testing and “medicine kits”, had helped regain control of the virus. The one thing the WHO failed to mention in its on-the-ground reporting is what was in those medicine kits.
The Wonders of Early Treatment
One thing that is that is clear is that many doctors in India try to treat covid-19 as early and as aggressively as possible, whereas many doctors in Europe and North America prescribe nothing more than paracetamol during the first seven days. As I’ve learnt from recent direct experience, this is the equivalent of laying down a red carpet for the virus and telling it to make itself at home and go wherever it wants, do whatever it wants.
“When we started seeing more cases, we decided to take up a door-to-door survey,” Bagalkot District Health Officer Dr Ananth Desai told New India Express in June. “When the health officials noticed people with symptoms during the survey, they tested them immediately and provided them with home isolation kits, which had medicines like Ivermectin, calcium and zinc tablets along with paracetamol. We advised the patients to start with the medication even before their Covid-19 test results came out. With these measures, we noticed that many patients recovered faster. This helped in increasing the recovery rate”.
Besides other factors such as lockdowns, travel restrictions and increased herd immunity, ivermectin has almost certainly played a part in this. But it’s impossible to know just how large a part. The fact that case numbers and deaths have tended to fall precipitously in regions where it is used widely, such as UP, New Delhi, Goa and Bihar, and have tended to remain high in regions where it isn’t, such as Kerala or Tamil Nadu (before it readopted ivermectin in June), does not constitute proof of causation. But when the same thing occurs in so many of the disparate parts of the world where ivermectin is used, a pattern begins to form that strongly supports ivermectin’s efficacy.
That doesn’t mean that it has a perfect record. In Mexico, for example, cases and deaths began surging once again in May, despite the fact that the Institute of Social Security (IMSS), which runs many of the country’s public hospitals, has been using IVM since January, albeit in very low doses. That said, it’s all but impossible to know how many doctors, public and private, are actually using the medicine. In May the newspaper Proceso reported that IMSS had repeatedly clashed with the federal government over its use of ivermectin. In June, the Mayor of Mexico City Claudia Scheinbaum announced that the city’s widespread use of IVM had reduced hospitalisations by up to 76%.
In early August, the results of the first large randomised control trial into IVM use for Covid-19 were released. And they showed “no effect whatsoever” on the trial’s outcome goals — whether patients required extended observation in the emergency room or hospitalization. However, as we noted in a previous article, this was a trial financed by the deeply compromised Gates Foundation, which is heavily invested in the new Covid vaccines, novel treatments and their manufacturers. And the person who lead the trial, Edward Mills, is a Gates Foundation employee. And the Canadian university that performed the trial, McMaster, is also a major recipient of Gates Foundation funding.
The results of another large RCT trialsinto ivermectin — the so-called PRINCIPLE trial taking place at Oxford University — should also be released in the coming months. Perhaps they will be more flattering.
The case for IVM was also not helped by the discovery of irregularities in a trial conducted in Egypt. That, together with the findings of the Together trial, is now cited by many media outlets as proof positive that ivermectin does not work against covid. To reach that conclusion, they steadfastly ignore the impressive results of many other small trials, the on-the-ground experience of untold thousands of medical practitioners and nurses, and the exceptionally low prevalence of covid in many of the places IVM is being used widely.
Ivermectin Comes Home, to Japan
As the Delta variant has swept through Asia, causing unprecedented devastation, more and more cities, regions and countries are considering authorising the use of ivermectin. They include Tokyo, where Haruo Ozaki, chairman of the city’s Metropolitan Medical Association, has called for ivermectin and the corticosteroid dexamethasone to be used due to the authorities’ failure to distribute vaccines in time. As Lambert pointed out a couple of days ago, Ozaki’s recommendation is for off-label use under “battlefield” conditions:
[OSAKI:] I am aware that there are many papers that suggest ivermectin is effective in the prevention and treatment of corona, mainly in Central and South America and Asia. There is no effective therapeutic drug, although it is necessary to deal with patients who develop it one after another. The vaccine is not in time. At such an imminent time, there is a paper that shows ivermectin is effective for corona, so it is a natural response for clinicians to try using it. Doctor-led clinical practice. That’s why many test papers came out.
On August 13, Ivermectin was added to the Tokyo Metropolitan Medical Association’s home treatment protocol. This is not to say that the whole nation of Japan — whose soil gave birth to the unique and extraordinary microorganism that produces the avermectins (from which ivermectin is derived) — has now embraced ivermectin. Nor is it clear how may doctors in Tokyo are actually using it. But the move could be an important first step, especially if covid-19 cases, hospitalisations and deaths fall.
Indonesia has also embraced ivermectin. On July 10, the Indonesian government secured the supply of COVID-19 treatment and created a website showing real time drug availability. Four days later the health regulator authorised the use of ivermectin for Covid-19. Then, on July 22, on July 22 Indonesia’s hospitals began using the drug. By the first week of August cases and deaths were falling.
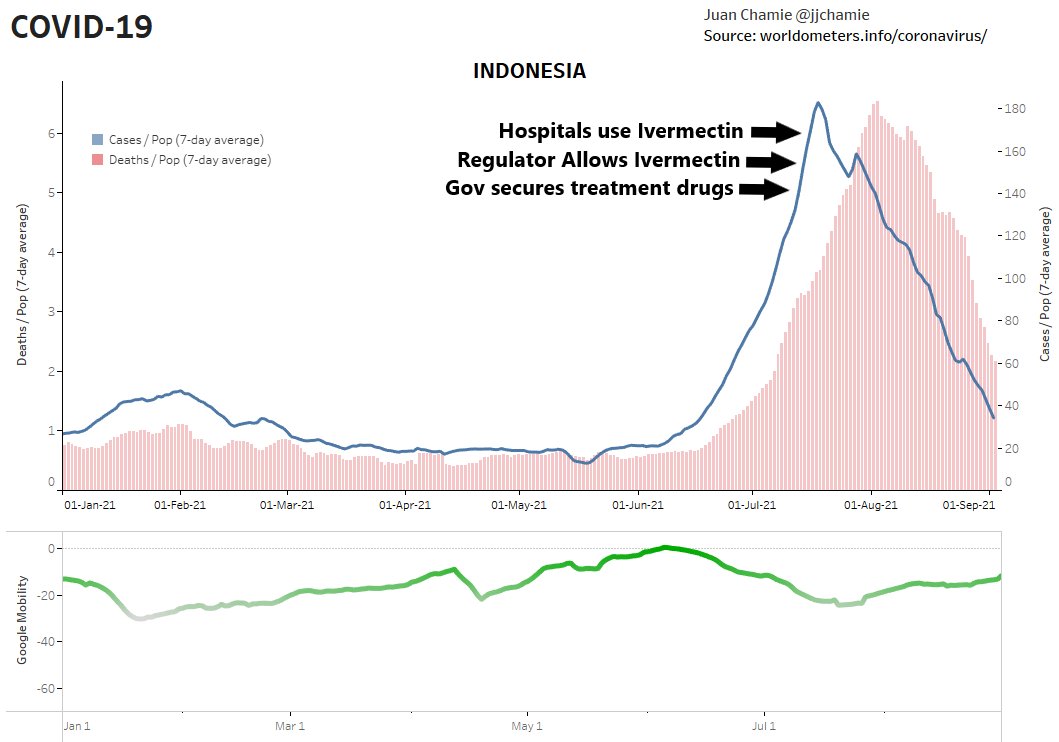
Meanwhile, Back in the USA…
Pfizer and Merck have announced new trials for their experimental oral antiviral drugs for COVID-19. Merck said in June that the U.S. government has already agreed to pay about $1.2 billion for 1.7 million courses of molnupiravir — working out at $705 per course of treatment — if it is proven to work and is given the green light by regulators. Pfizer, meanwhile, said that if its trial of its “affordable” early treatment pill is successful, it will file for emergency approval between October and December this year.
If the authorisation process is anything like the process employed for Gilead’s Remdesivir, which is included in standard-of-care protocols throughout Europe and the US despite offering next to no real benefits (according to the WHO), and Pfizer’s booster vaccine, Pfizer will be raking in even more money from Covid by the year’s end.
Being able to take an oral antiviral therapeutic for SARS-CoV-2 at home would be a “game changer,” according to Albert Bourla, Pfizer’s CEO.
As I posited in a previous article, one of the main reasons why there has been such fierce opposition to ivermectin is that large pharmaceutical companies are developing their own antiviral therapies that will have to compete directly with ivermectin. Another reason is that if ivermectin were approved as a covid-19 treatment, it could threaten the emergency use authorisation granted to covid-19 vaccines and novel treatments, although the recent approval of Pfizer’s COMIRNATY vaccine may have changed that.
When financial returns are the primary priority in a health care system, this is what you get. Everything is geared to churning out brand new, barely tested experimental medicines as quickly as possible, with scant communication of what potential side effects they may produce. Throw in monopoly control of intellectual property and you have the perfect business model. Whether the new medicines work or not or do more harm than good, they will cost an arm and a leg. And their manufacturers will probably be protected from liability. The patients’ health, well being and welfare are barely an afterthought.


No comments:
Post a Comment